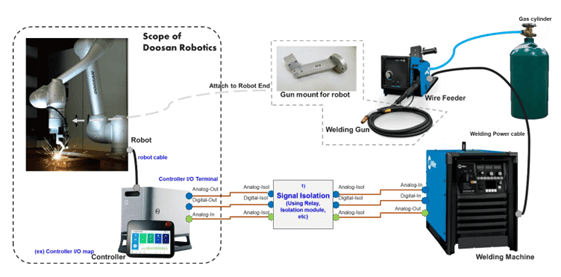
Getting Started with Cobot Welding
What is a Cobot, and Can You Work with One?
Cobots are easier to use than traditional industrial robots (IRs) because they include options for hand guiding, and have generally more simple and intuitive programming. This makes them a lot more accessible to people who do not have a robotics or programming background. Because they can be hand manipulated, the experience of programming is more physical than traditional coding. Sometimes, programing a cobot is described as the user speaking human language to the robot, rather than us learning the robot’s language.
To program a cobot welding application, it is far more important that the user be a competent welder, rather than robotically savvy. Power/mation is happy to get an operator, engineer, or welder up to speed with our cobots.

Benefits of Cobot Welding
Easy to use
Flexible
Increase Productivity
Safety in mind
What Makes an Ideal Application?
Cobot welding excels in scenarios involving small parts in large quantities, such as brackets, stands, and small automotive components. It is equally valuable for larger parts that require exceptional consistency, including large frames, agricultural items, and metal forms. Cobot welding is particularly advantageous for tasks involving long, straight seams that would be physically demanding for a human welder. For these longer or larger weld paths, cobots can be placed on a 7th axis, although it’s important to note that the 7th axis is not collaborative in nature.
Lots of Options in Between!
Cobot welding is versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. If your skilled workforce encounters welding challenges, cobot technology can be evaluated as a solution.
Examples of Cobot Welding

Hand-Guided Welding – In this example, the operator is hand-guiding the cobot’s welding path using the teach pendant on the floor. Multiple small parts are being welded simultaneously on a larger welding table.


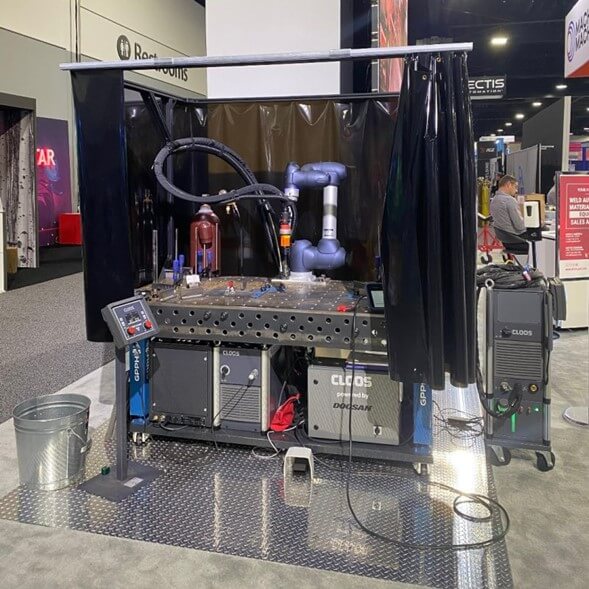
Small/Medium Weld Cell – In this scenario, a small to medium-sized weld cell is employed, with protective measures in place to prevent issues such as weld splatter or operator interference. The system incorporates various accessories, including a hose package and a weld table with adjustable bracketing.
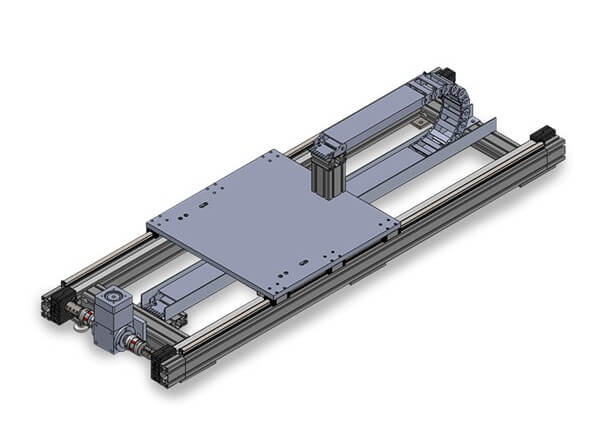
7th Axis (Robot Transfer Unit) – Macron Dynamics – In this scenario, a small to medium-sized weld cell is employed, with protective measures in place to prevent issues such as weld splatter or operator interference. The system incorporates various accessories, including a hose package and a weld table with adjustable bracketing.
How does Cobot Welding Work?
Current Capabilities
- Cobot welding primarily involves MIG welding, with stick or spot welding not currently available with cobots.
Key Components
A cobot welding system requires the following main components:
- Cobot
- Weld Table
- Weld Torch designed for robotic welding
- Weld power supply and wire feeder
Get Started
To kickstart your cobot welding journey:
- Discuss interface and welder options with Power/mation.
- Provide detailed part information, including drawings, images, measurements, or samples for evaluation.
- Schedule training sessions with Power/mation to prepare your team for successful cobot welding. Additionally, consider contacting your local welding distributor for supplementary welding training as needed.
Submit the Form Below to Start the Conversation